化学システム工学における材料・デバイスMaterials and Devices in Chemical System Engineering
化学システム工学専攻Department of Chemical System Engineering
「化学システム工学」という言葉には、これまでの化学や化学工学の枠を超えたアプローチを目指すという想いが込められています。環境、エネルギー、医療などに関するさまざまな課題に対して、化学を基盤に、システム的思考を持って臨むことで、課題解決への具体的かつ永続的なビジョンを示すことを目指しています。
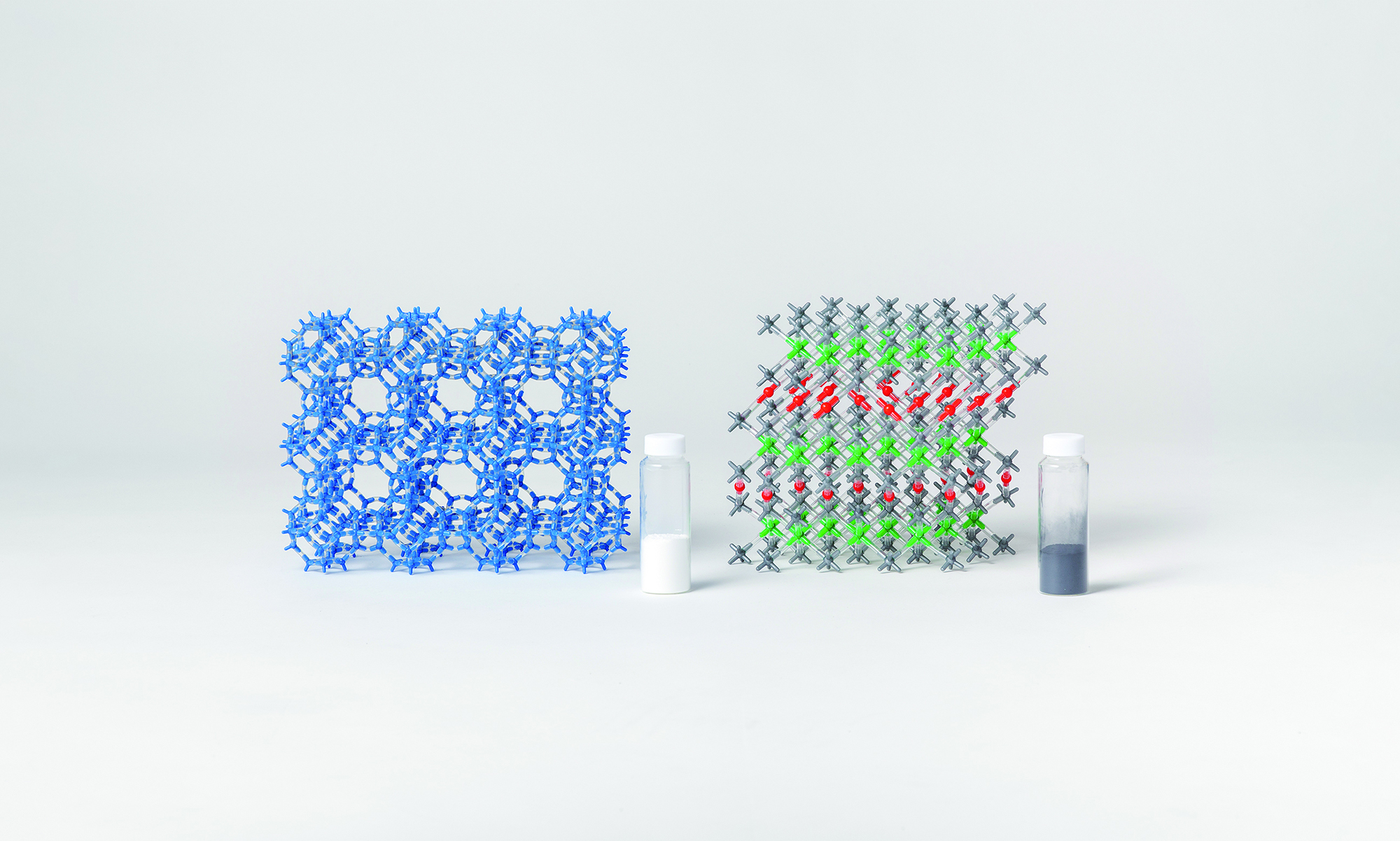
環境・エネルギー問題を解決するための材料・デバイスの例として、リチウムイオン電池の電極材料であるコバルト酸リチウムと環境の浄化や保全に幅広く使用されているゼオライトを展示しています。
現代の複雑化した問題を解決するためには、システム・デバイスを俯瞰し、そのなかでの材料の位置づけを行った上で、新たな機能性材料の適用およびその反応機構の正しい理解に基づく最適化が不可欠となります。
左)ゼオライトナノ粒子と結晶模型
寸法:150×30φ, 80×40(ゼオライトナノ粒子), 150×150×150(結晶模型)
所蔵:東京大学 大学院工学系研究科 化学システム工学専攻
人工的に合成されたゼオライトの結晶。結晶中に分子サイズの空隙が空いており、分子をふるい分けることができる。その特性を活かしてイオン交換剤・触媒・吸着剤などとして、幅広い分野で使用されている。
右)コバルト酸リチウムと結晶構造
寸法:150×150×150(結晶模型)
所蔵:東京大学 大学院工学系研究科 化学システム工学専攻
リチウムイオン電池の電極材料であるLiCoO2の結晶構造。CoO2層間をリチウムイオンが移動して、充電と放電を行うことができる。この化合物を初めて合成したJ. B. Goodenough教授は、2019年ノーベル化学賞を受賞した。
パネル
寸法:594×841
所蔵:東京大学 大学院工学系研究科 化学システム工学専攻
The term “Chemical System Engineering” details our ambition to approach issues beyond the boundaries of chemistry and chemical engineering to date. We can demonstrate a concrete and permanent vision of the solution to various problems related to the environment, energy, medical care and so on by systematic thinking based on chemistry.
LiCoO2 for the electrode material of lithium-ion batteries and ZEOLITES for preserving and purifying the environment are exhibited as representatives of materials and devices for solving environmental and energy problems.
In order to solve complicated problems, we need a bird’s-eye view of the systems and devices as well as the understanding of position of materials for applying new functional materials and their optimization by the correct understanding of reaction mechanisms.
Left)Zeolite nanoparticles and Crystal structure model
Size: 150×30φ, 80×40(Zeolite nanoparticles), 150×150×150(Crystal structure model)
Collection: Department of Chemical System Engineering, School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo
Right) LiCoO96 and Crystal structure model
Size: 150×150×150(Crystal model)
Collection: Department of Chemical System Engineering, School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo
LiCoO2 for the electrode material of lithium-ion batteries and zeolites widely used to preserve and purify the environment are exhibited as representatives of materials and devices for solving environmental and energy problems.
Panel
Size: 594×841
Collection: Department of Chemical System Engineering, School of Engineering, The University of Tokyo

